How to Measure Rainfall? Uncover the Precision Methods
To measure rainfall, use a rain gauge. Place it in an open area away from obstructions.
Rainfall measurement is crucial for various sectors like agriculture, meteorology, and hydrology. Knowing how to accurately measure rainfall can provide valuable data for weather forecasting, water resource management, and flood control. By using a rain gauge, which is a simple yet effective tool, precipitation levels can be monitored over a specific period.
This data helps in understanding rainfall patterns, drought prediction, and overall climate trends. Whether for scientific research or everyday purposes, the process of measuring rainfall plays a vital role in ensuring preparedness and informed decision-making across different industries.

Credit: housing.com
The Essence Of Measuring Rainfall
Measuring rainfall is an essential task that provides crucial information about the climate, environment, and water resources. Rainfall is a natural phenomenon that can have a significant impact on our daily lives. It is essential to measure rainfall accurately to understand its effects on various aspects of life, such as agriculture, urban planning, and water management.
The Importance For Agriculture
Agriculture is one of the most critical sectors that rely heavily on rainfall. Measuring rainfall is crucial for farmers to determine the timing of planting and harvesting crops. It helps them to plan their irrigation systems and manage their water resources effectively. Accurate rainfall data can also help farmers to decide on the types of crops to grow and the amount of fertilizer to use.
Impacts On Urban Planning
Rainfall can also have a significant impact on urban planning. Cities need to plan their drainage systems and infrastructure to prevent flooding during heavy rainfall. Measuring rainfall can help urban planners to determine the potential risks and develop strategies to manage them. It can also help them to identify areas that are vulnerable to flooding and plan accordingly.
Moreover, rainfall data is also critical for water management. It helps water managers to monitor the water levels in rivers, reservoirs, and groundwater aquifers. This information is essential for planning and managing water resources effectively.
Measuring Rainfall
There are several methods for measuring rainfall, including:
- Rain gauges
- Doppler radar
- Satellite remote sensing
Rain gauges are the most common method used for measuring rainfall. They are simple devices that consist of a funnel and a container. The funnel collects the rainwater, which then flows into the container. The amount of rainfall is measured by the depth of water in the container.
In conclusion, measuring rainfall is essential for understanding its impact on various aspects of life, such as agriculture, urban planning, and water management. Accurate rainfall data can help us to plan and manage our resources effectively, and mitigate the potential risks associated with heavy rainfall.
Historical Methods Of Rainfall Measurement
Ancient Techniques
Ancient civilizations used various methods to measure rainfall, including simple containers to collect water and observe the depth of the collected water over a period of time.
Development Of Modern Gauges
The development of modern rain gauges began in the 15th century with the invention of the tipping bucket rain gauge by Korean scholars. This technology evolved over time, leading to the creation of standardized and more accurate rain gauges.
Standard Rain Gauges
Standard rain gauges are essential tools for measuring rainfall accurately. With their simple design and easy-to-read measurements, they provide reliable data for meteorologists and weather enthusiasts alike. By following proper techniques, you can ensure precise measurements and contribute to our understanding of rainfall patterns.
Types And Designs
When it comes to measuring rainfall, standard rain gauges are commonly used. These gauges come in various types and designs, each with its own advantages and suitability for different environments.
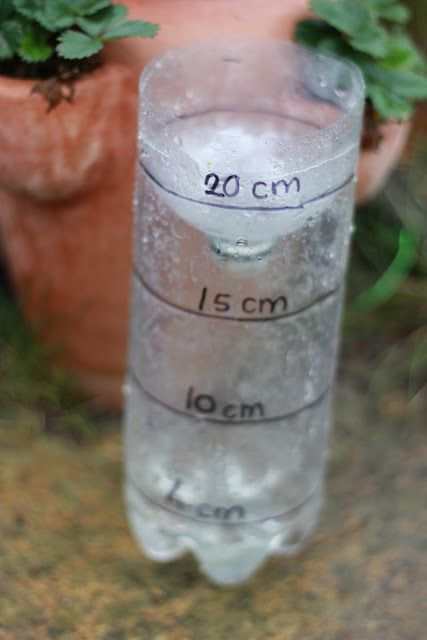
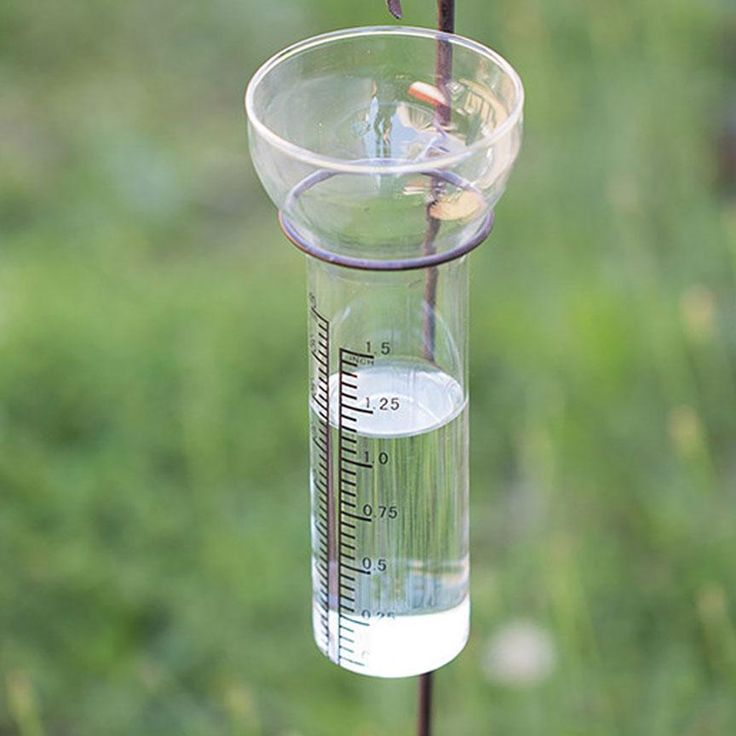
One of the most common types of standard rain gauges is the cylindrical gauge. It consists of a transparent cylindrical container, usually made of glass or plastic, with markings indicating the amount of rainfall in inches or millimeters. This design allows for easy visualization and measurement of rainfall.
Another type is the weighing rain gauge, which measures rainfall by weighing the collected water. This gauge usually has a funnel-shaped top that directs the rainwater into a container attached to a sensitive scale. The weight of the water collected is then converted into rainfall measurements.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation of standard rain gauges is crucial to ensure accurate measurements. Here are some best practices to follow:
1. Location: Place the rain gauge in an open area away from obstructions such as buildings or trees. This ensures that rainwater falls directly into the gauge without interference.
2. Level Ground: Make sure the ground where the rain gauge is installed is level. This prevents any tilting or unevenness that could affect the measurements.
3. Height: Position the rain gauge at an appropriate height, ideally around one meter above the ground. This helps to minimize splashing or evaporation of the collected water.
4. Clear Surroundings: Keep the area around the rain gauge clear of any debris or vegetation. This prevents any interference with the rainfall measurement and reduces the risk of contamination.
5. Regular Maintenance: Regularly check and clean the rain gauge to ensure accurate readings. Remove any leaves, dirt, or other debris that may accumulate over time.
By following these installation best practices, you can ensure that your standard rain gauge provides reliable and precise measurements of rainfall.
In conclusion, standard rain gauges offer a simple and effective way to measure rainfall. Understanding the different types and designs, as well as implementing proper installation practices, will help you obtain accurate data for various purposes, such as weather monitoring, agriculture, or research.
The Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
When it comes to measuring rainfall, one of the most commonly used devices is the tipping bucket rain gauge. This simple yet effective instrument provides accurate and reliable measurements of rainfall. In this section, we will explore the design and functionality of the tipping bucket rain gauge, as well as the important aspects of calibration and maintenance.
Design And Functionality
The tipping bucket rain gauge consists of a funnel-shaped collector that directs rainfall into a small bucket with a pivot point in the middle. As the rainwater fills the bucket, it eventually reaches a tipping point, causing the bucket to empty and simultaneously triggering a switch. This switch, often a reed switch, sends an electrical signal to a data logger, recording the amount of rainfall.
The design of the tipping bucket rain gauge allows for accurate measurements, as each tip of the bucket represents a predefined amount of rainfall, typically 0.2 mm or 0.01 inches. This makes it easy to convert the number of tips into a total precipitation value. Additionally, the bucket’s dual chambers ensure that while one side fills with rainwater, the other side empties, allowing for continuous measurement without interruption.
Calibration And Maintenance
To ensure accurate measurements, regular calibration and maintenance of the tipping bucket rain gauge are essential. Calibration involves comparing the readings of the rain gauge with those of a known standard, such as a high-quality reference rain gauge or a weather station. If any discrepancies are found, adjustments can be made to the tipping mechanism to ensure accurate readings.
Maintenance of the tipping bucket rain gauge includes keeping the collector free from debris and obstructions, as well as regular cleaning to prevent any buildup that may affect the device’s functionality. Additionally, it is important to check the switch and wiring for any signs of damage or wear, as these can affect the accuracy of the measurements.
In conclusion, the tipping bucket rain gauge is a reliable and efficient instrument for measuring rainfall. Its simple design and functionality make it a popular choice for meteorological monitoring stations and home weather enthusiasts alike. By understanding its design, performing regular calibration, and maintaining the device properly, accurate measurements of rainfall can be obtained for a variety of applications.
Weighing Gauges And Siphoning Systems
When it comes to measuring rainfall, two commonly used methods are weighing gauges and siphoning systems. These techniques provide valuable data for weather monitoring and forecasting, aiding in various applications such as agriculture, hydrology, and climate research.
Advantages Of Weighing Gauges
Weighing gauges offer several advantages in measuring rainfall. They are highly accurate and can capture even light precipitation. Additionally, they are relatively simple to maintain and operate, making them a cost-effective solution for long-term rainfall measurement.
Understanding Siphoning Mechanisms
Siphoning systems employ a different approach to measure rainfall. They function by using a siphon to transfer water from a collection funnel to a measuring container. Understanding the siphoning mechanism is crucial in ensuring accurate and reliable rainfall data.
Optical Rain Gauges And Disdrometers
Optical rain gauges and disdrometers are advanced tools to measure rainfall accurately.
Technology Behind Optical Gauges
Optical gauges use light to detect raindrops and measure their size.
These gauges provide real-time data on rainfall intensity and distribution.
Disdrometers In Detail
Disdrometers are specialized instruments that analyze raindrop size and velocity.
They are crucial for studying precipitation patterns and storm dynamics.
Automated Weather Stations
Automated Weather Stations provide accurate measurements of rainfall using specialized sensors. These stations employ advanced technology to collect and analyze data, allowing meteorologists to track precipitation patterns with precision and reliability.
Automated Weather Stations are crucial for accurate rainfall measurements.
Integration With Rainfall Measurement
Automated Weather Stations integrate seamlessly with rainfall measurement systems.
Data Collection And Transmission
Data collection and transmission are automated processes in weather stations.

Credit: www.wikihow.com
Accuracy And Calibration
Accuracy and Calibration are essential in measuring rainfall effectively. Proper calibration ensures precise data collection.
Standard Calibration Procedures
Calibrating rain gauges regularly maintains accuracy. Follow manufacturer guidelines for calibration.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issues like debris blockage can affect accuracy. Clean rain gauges frequently to prevent inaccuracies.
Rainfall Data Analysis
To measure rainfall, various methods such as rain gauges, weather radar, and satellites are used. Rain gauges, the most common method, collect and measure precipitation. Weather radar detects rainfall by sending out radio waves, while satellites use remote sensing to monitor precipitation patterns.
Interpreting The Measurements
Applications In Weather Forecasting
Rainfall data analysis involves understanding and utilizing rainfall measurements. Interpreting these measurements is crucial for various applications, including weather forecasting.
Interpreting The Measurements
When analyzing rainfall data, consider factors like duration and intensity.
Applications in Weather Forecasting
In weather forecasting, rainfall data helps predict future weather patterns accurately.
Analyzing rainfall data involves understanding measurements like duration and intensity.
Rainfall data is essential for accurate weather forecasting.
Innovations In Rainfall Measurement
Innovations in Rainfall Measurement have transformed the way we understand and track precipitation. Emerging technologies and the future of precipitation tracking are shaping the way we measure and analyze rainfall data.
Emerging Technologies
Advancements in rainfall measurement technologies have revolutionized the accuracy and efficiency of collecting precipitation data. Remote sensing technologies, such as weather radar and satellite imagery, provide real-time information on rainfall patterns across large geographic areas. These technologies enable meteorologists and researchers to monitor and predict rainfall events with remarkable precision.
The Future Of Precipitation Tracking
The future of precipitation tracking is marked by the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and advanced data analytics. IoT-enabled rain gauges and weather stations offer continuous, localized rainfall measurements, allowing for detailed analysis of precipitation trends. Additionally, the use of artificial intelligence algorithms enhances the accuracy of rainfall predictions, leading to more effective disaster preparedness and water resource management.

Credit: housing.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Is Rainfall Measured?
Rainfall is typically measured using a rain gauge, which collects and measures the amount of precipitation in a specific area.
What Is A Rain Gauge?
A rain gauge is a tool used to measure the amount of rain that falls in a specific location over a certain period of time.
How Accurate Are Rain Gauges?
Rain gauges can be very accurate when used correctly, but there are some factors that can affect their accuracy, such as wind and evaporation.
What Are The Different Types Of Rain Gauges?
There are several types of rain gauges, including standard gauges, tipping bucket gauges, and weighing gauges, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
Why Is It Important To Measure Rainfall?
Measuring rainfall is important for a variety of reasons, including tracking weather patterns, predicting floods and droughts, and monitoring water resources.
Conclusion
Measuring rainfall is vital for various industries and activities. By using accurate tools and techniques, such as rain gauges and weather radars, accurate data can be obtained. This information is crucial for agriculture, water resource management, and climate studies. Understanding rainfall patterns helps in making informed decisions and planning for the future.